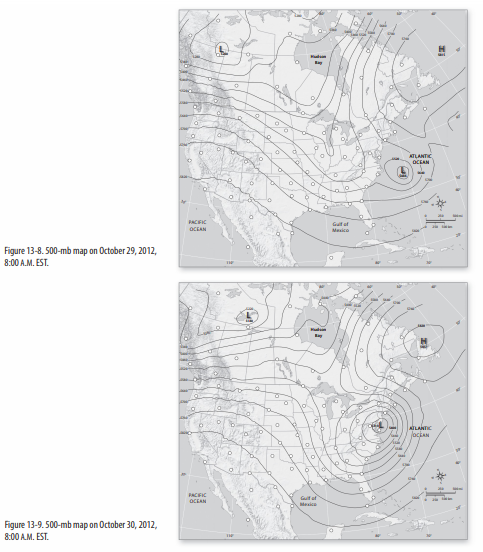
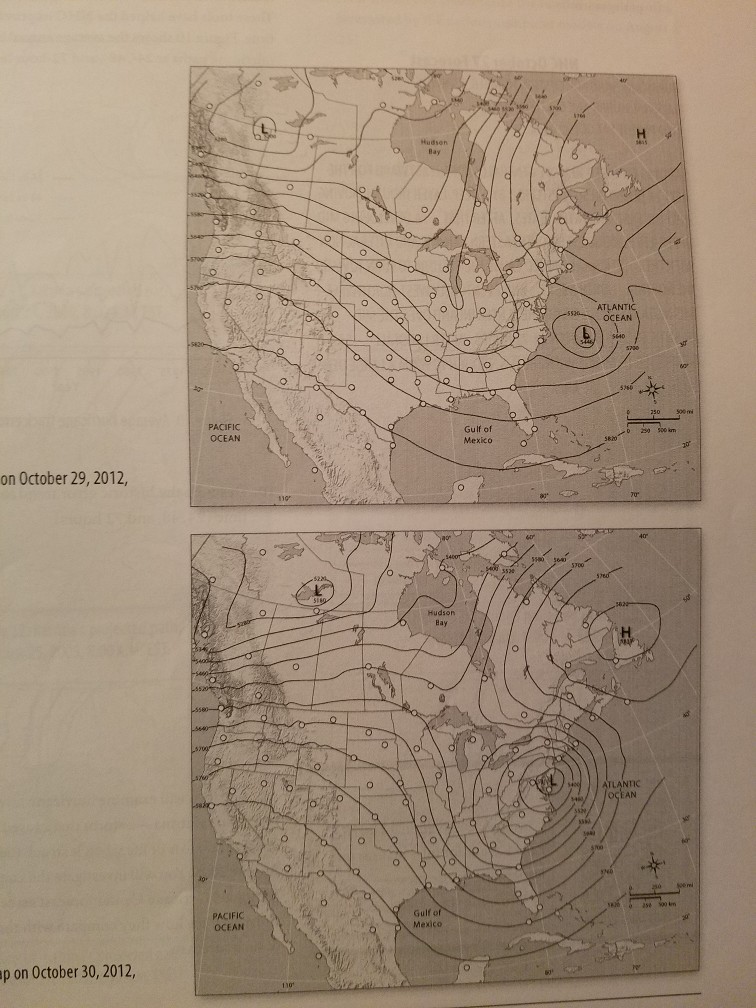
O D ATLANTIC OCEAN OCEAN Mexico Figure 13-8500-mb map on October 29 2012 800 AMEST. Dashed curves represent two values of -f which becomes inertial wind when VO.
Solved 8 Assuming Gradient Wind Flow Draw The Winds Around The High Course Hero
Circle the upper-air inversion layer on the Paducah and Topeka environmental temperature profiles.
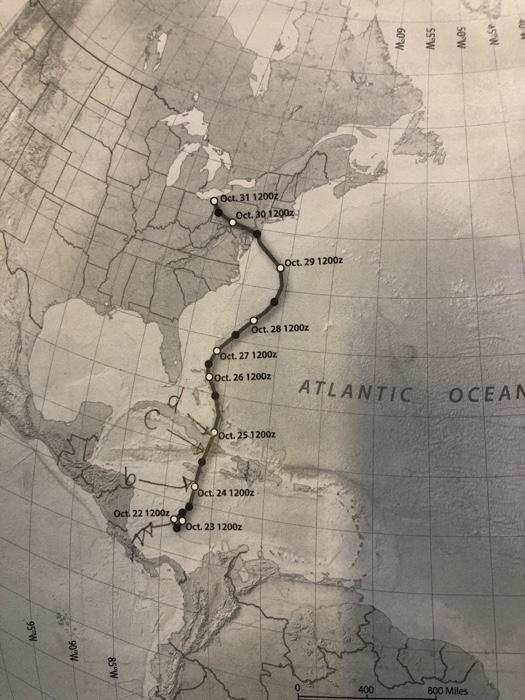
. How did the circulation around these pressure centers influence Sandys path. ϕ v 2 r 0 1 ρ Δ P Δ r. Winds in upper atmosphere.
Wind flowing parallel to pressure isobars or contours with low pressure on the left of the observer in the Northern Hemisphere. Assuming gradient wind flow draw the winds around the high pressure cell in the Atlantic on October 29 and 30. Use this data T2 to estimate the tornado winds.
How did the circulation around these pressure centers influence Sandys path. Differences between actual wind magnitude and that of the gradient wind m s 1 shaded color bar at top are shown for a steady contour b nonsteady contour c steady natural and d nonsteady natural gradient winds at the 250-hPa levelThe data are 1 1 latitudelongitude filtered GFS forecast grids averages of the 24- and 27-h. A 4 points Assuming geostrophic and frictionless flow please draw vectors for the pressure gradient and coriolis forces for the Northern Hemisphere.
For anticyclonic values of R a zero radical produces the following rela- tionship as a lower limit for the anomalous solution. I should point out however that the geostrophic wind is an idealized wind. The components of the thermal wind vector along the x and the y axes may then be written as ut RfdTdyp lnpop1 vt RfdTdxp ln pop1.
Pressure gradient force centrifugal force 0. Please explain why or why not. How did the circulation around the pressure centers influence Sandys path.
Stronger than surface air bc no friction. Compared to geostrophic winds gradient winds feature a balance between the Coriolis force the pressure gradient force and the centrifugal force. How would you charact.
Assuming gradient Wind flow draw the winds around the high-pressure cell in the Atlantic on October 29 and 30th. Flow around high and low pressure centers in the two hemispheres upper air and surface For the Northern Hemisphere. Time 0 is when the tornado was closest to the weather station.
In other words for a tornado. Assuming gradient wind flow draw the winds around the high pressure cell in the Atlantic on October 29 and 30. Assuming gradient wind flow draw the winds around the high pressure cell in the Atlantic on October 29 and 30.
The pressure gradient force PGF the Coriolis Force and friction. It never perfectly occurs in nature. ATLANTIC OCEAN D RACER OCEAN Figure 13-9500-mb map on October 30.
The data below is a pressure trace near a large tornado. How did the circulation around these pressure centers influence Sandys path. Velocity such that the pressure gradient Coriolis and centrifugal force acting in the area are in balance.
Explain how the path of the storm might have influenced the storm-surge heights seen in Figure 13-18. The speed and direction of the wind is governed by three forces. PGF is the force.
PGF Coriolis b 2 points Are geostrophic winds a good approximation for surface winds. Mar 18 2022 0907 AM. 4 For anomalous gradient.
Velocity is generally five to 30 miles per hour and. Assuming gradient wind flow draw the winds around the high pressure cell in the Atlantic on October 29 and 30. View raw image.
Wind created by differing barometric pressures between high- and low-pressure systems. Equation 1266 is the well-known thermal wind equation which controls the vertical variation of the wind with height in a region where there exists a horizontal gradient of temperature. How did the circulation around these pressure centers influence Sandys path.
Mar 24 2022 0529 AM. No geostrophic winds are not valid at the surface because isobars are rarely. The second version of the gradient wind equation for cyclonic flow shows why the speed of the gradient wind in this case is less than the speed of geostrophic wind for the same pressure gradient magnitude.
Winds typically blow along isobars even if they are curved but a different name is needed because the force balance includes one more component. 2 Ω v sin. Parallel to isobars from High to Low.
The curving motion introduces a centrifugal outward fleeing force. 80 40 0 3205580 40 387 5700. If we assume that the winds are in or near geostrophic balance we can use the isobars or the height contours as indicators of wind flow instead of streamlines.
The flow within a tornado is due to the combination of the pressure gradient and centrifugal forces. Anomalous solution to eq 2 is eq 3b. Draw the surface winds around the eye of the Northern Hemisphere hurricane depicted in the picture below Fig 13-1 2.
The centrifugal effect can be felt when turning through a curve in a car. A geostrophic wind becomes a gradient wind when the wind begins flowing through curved height contours. Assuming gradient wind flow draw the winds around the high pressure cell in the Atlantic on October 29 and 30.
Assuming gradient wind flow draw the winds around the high pressure cell in the Atlantic on October 29 and 30. The pressure gradient results in a net force that is directed from high to low pressure and this force is called the pressure gradient force. Gradient winds are winds flowing along curved isobars.
Because of the energy surplus at low latitudes for example the air there is warmer. Differences in air pressure and the pressure gradient force are caused by the unequal heating of the Earths surface when incoming solar radiation concentrates at the equator. Draw the surface winds around the eye of the Northern Hemisphere hurricane depicted in the picture below Fig 13-1 2.
Assuming gradient wind flow draw the winds around the high pressure cell in the Atlantic on October 29 and 30. Ms showing the double solution for gradient wind equation during anticyclonic flow. Assuming gradient Wind flow draw the winds around the high-pressure cell in the Atlantic on October 29 and 30th.
Figure 13-4 shows how. The gradient wind is a balance of the Pressure Gradient Force centrifugal and Coriolis. As you know near the surface of the earth.
The force actually responsible for causing the movement of air though is the pressure gradient force. Figure 13-4 shows how. How did the circulation around these pressure centers influence on this path.
Regardless of the strength of the pressure-gradient force you can try varying it in the interactive force diagram the end result is geostrophic balance with a stronger pressure-gradient force leading to faster wind speeds. This is superior to using streamlines because the spacing of the isobars or height contours the gradient is proportional to the geostrophic wind speed. What forces act on air and cause it to flow.
Solved Assuming Gradient Wind Flow Draw The Winds Around Chegg Com

Solved Anes 8 Assuming Gradient Wind Flow Draw The Winds Chegg Com
Solved 8 Assuming Gradient Wind Flow Draw The Winds Around The High Course Hero

Solved Assuming Gradient Wind Flow Draw The Winds Around Chegg Com
Solved Assuming Gradient Wind Flow Draw The Winds Around Chegg Com
Solved 8 Assuming Gradient Wind Flow Draw The Winds Around The High Course Hero
Solved Anes 8 Assuming Gradient Wind Flow Draw The Winds Chegg Com
Solved 8 Assuming Gradient Wind Flow Draw The Winds Around The High Course Hero
0 comments
Post a Comment